The SpaceX Crew-9 mission, carrying NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Alexander Gorbunov, was specifically launched to provide a safe return option for Williams and Wilmore.

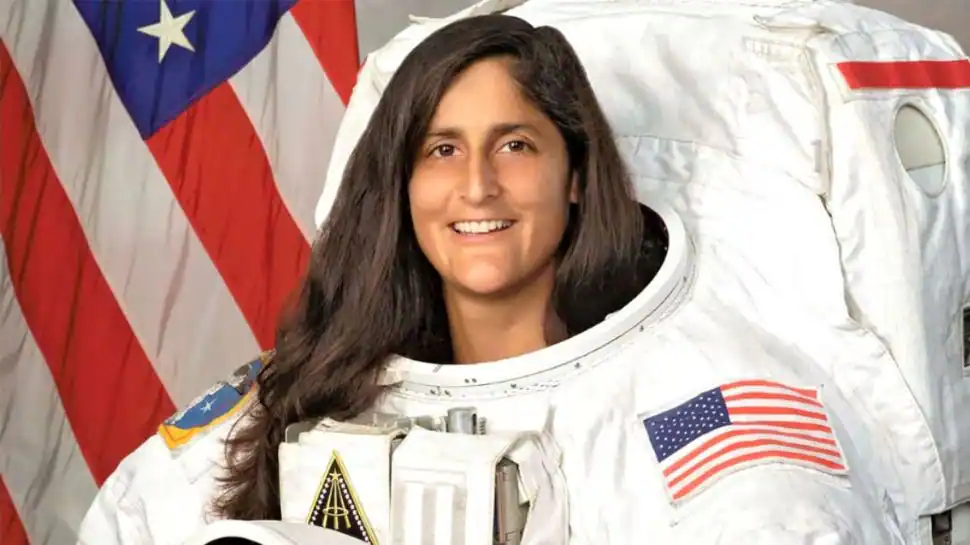
Rescue of Sunita Williams and Wilmore
Despite the successful docking of the space X Dragon rescue space craft at the international space station (ISS), NASA astronaut Sunita Williams will not be returning to earth immediately.
The rescue mission was launched in response to the delayed stay of Williams and Wilmore, due to issues with the Boeing’s Starliner spacecraft.
Also Read: HCL employee dies of cardiac arrest in office washroom in Maharashtra
Sunita Williams with fellow astronaut Butch Wilmore, was originally scheduled to return to earth after a brief stay on the ISS as part of Boeing’s first crewed Starliner flight.
However, technical problems with the Starliner, including thruster issues and helium leaks, led Nasa to deem the spacecraft too risky for a crewed return journey.
Factors affecting their extended stay
- * Crew rotation logistics: Nasa has carefully planned crew rotations to maintain continuous operations on the ISS. An immediate return would disrupt these schedules and potentially leave the station understaffed.
- * Crew rotation logistics: Nasa has carefully planned crew rotations to maintain continuous operations on the ISS. An immediate return would disrupt these schedules and potentially leave the station understaffed.
- * Preparation time: The astronauts need time to properly hand over their responsibilities and prepare for the return journey, which includes physical conditioning for re-entry and readjustment to Earth’s gravity.
During her extended stay, Williams has assumed command of the ISS, showcasing her leadership skills and adaptability in the face of unforeseen circumstances. This situation highlights the complexities and challenges of space missions, as well as the importance of having flexible backup plans in place.
Williams’ extended mission will likely provide valuable data on long-duration space habitation, further contributing to future space exploration efforts.